Oxygen And Its Compounds









Oxygen And Its Compounds
Oxygen (0): Oxygen (atomic number 8; atomic weight 15,9994; and electronic configuration 2, 6), under ordinary conditions, is a colourless, odourless gas. The most abundant of all the elements in the earth's crust, it forms about one-fifth (by volume) of the atmosphere.
It is a most useful element; both combustion and respiration involve oxygen. It has many uses. Oxyacetylene burners produce very high temperature flames for cutting and welding metal. When steel is being made, oxygen is used to remove the impurities from the molten iron, Pure oxygen, stored in cylinders, is used to support breathing- to help patients in hospitals, and for high altitude or underwater work. Space rockets have to carry liquid oxygen in order to burn their fuels in space; in manufacturing liquid rocket fuels, liquid oxygen is used to burn either liquid hydrogen or kerosene.
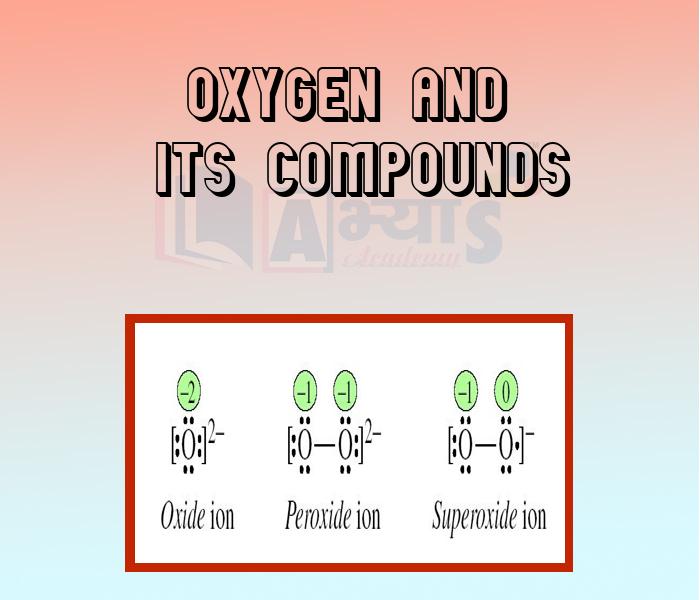
The oxygen cycle is an important natural process. Respiration and commercial activities transform oxygen to carbon dioxide and other gases. Photosynthesis by green plants uses carbon dioxide to release oxygen.Ozone: Ozone is a powerful oxidising allotropic form of oxygen. The ozone molecule contains three atoms (0). Having a characteristic, pungent odour, ozone is irritating to mucous membranes and toxic to human beings and lower animals. Ozone is formed when electrical apparatus produces sparks in air.
Ozone is a powerful oxidising agent. In the presence of water, it is a powerful bleaching agent. Ozone is used in the treatment of drinking water supplies.
Ozone occurs to a variable extent in the earth's atmosphere. Near the surface, the concentration is usually 0.02-0.03 ppm. At vertical elevations above 20 km, ozone is formed by photochemical action on atmospheric oxygen. Atmospheric ozone acts as a selective filter for ultraviolet rays, stopping the harmful ones and letting the beneficial ones by .
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
My experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice
